Water in the World – Going with the Flow
-
Water
-
Forests
-
Human Impacts
-
Ecosystem Services
-
Science and Geography
-
Field Work

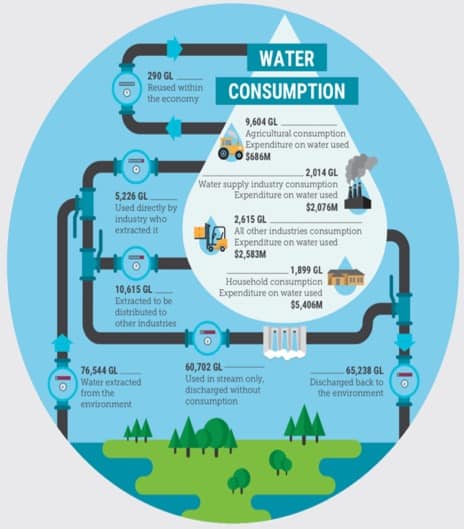

Excursion Program Overview
Watch this short video of program highlights.
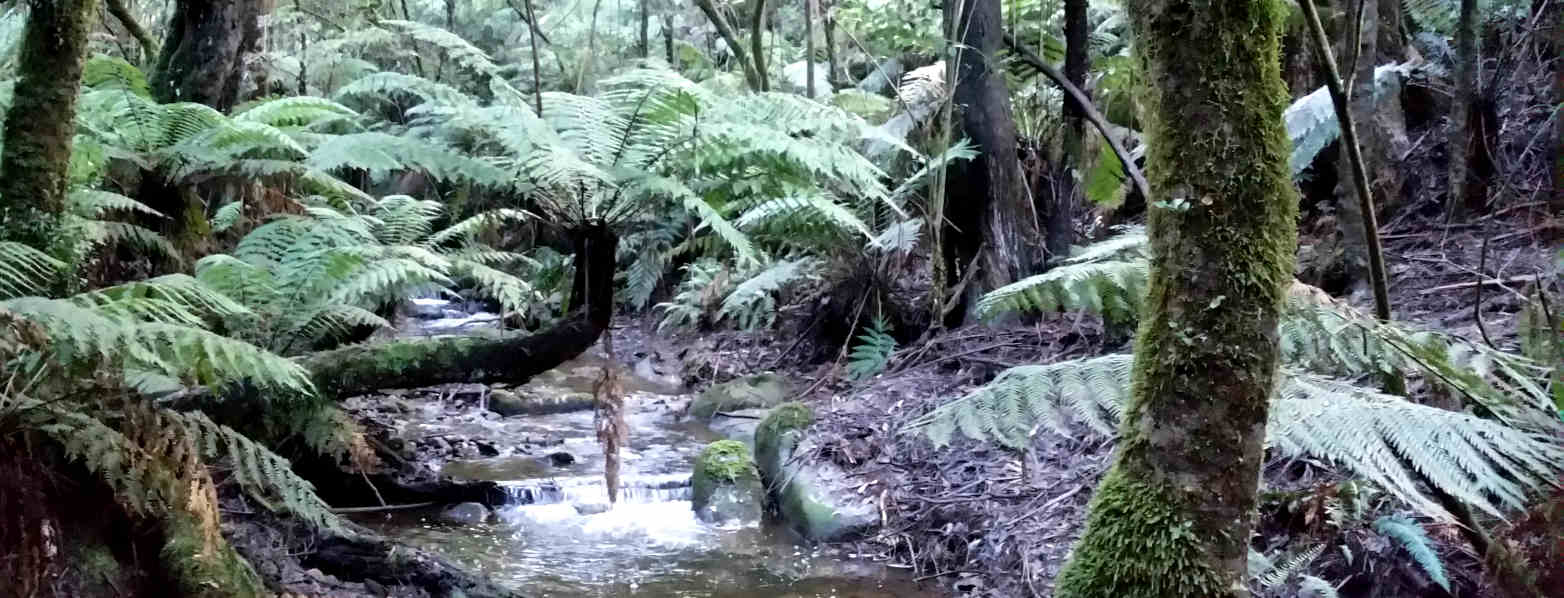
The Toolangi State forest is critical to Melbourne’s water supply. During this excursion, students learn how Toolangi State Forest contributes to creating, collecting, storing and filtering water, as well as the natural and human influences on water movement and quality such as logging, bushfires, weeds and climate change.
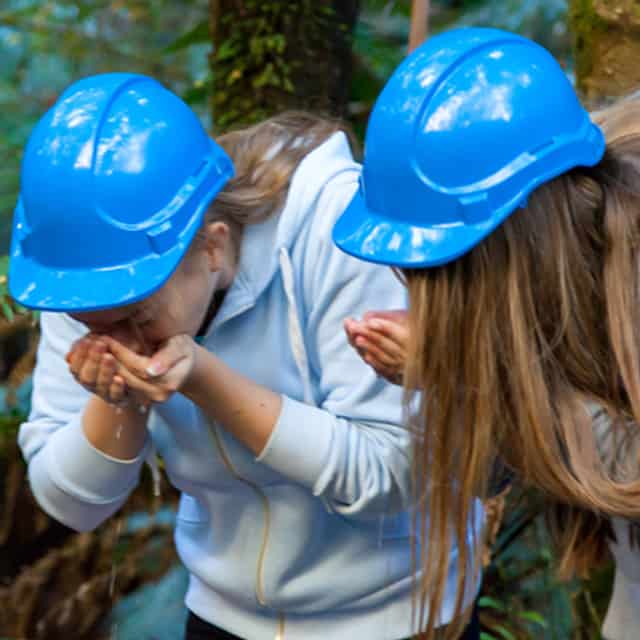
Students perform field work that compares water quality from a number of different sources testing for Salinity, Hardness, Total Disolved Solids, pH, Disolved Oxygen as well as aquatic invertebrates. The introduction of the exploration of water bugs has been a big hit with the students! We also explore water uses, water values for a range of plants and animals, the water outlook and ways schools and the community can save water which is critical now many parts of Victoria are in drought.
Inclusions and Notes
Equipment supplied by Gould League: Safety helmets worn by all participants; workbook and all tools required for fieldwork data collection.
Equipment needed: A chartered bus (which is required to remain with the group at all times). First aid kit, sun screen, insect repellent and PPE including hand sanitiser to kill viruses, bacteria and other micro organisations. Please note that our Gould League educators will travel on your bus for the duration of your program time. We ask schools to ensure when booking coaches that 1 one seat is allocated for each group booked as they will provide commentary on the bus to students and guide the bus drivers. Please advise the Bookings Manager if there is no room on the coach for our educators, and travel fee of $0.88 per km will be added to your final invoice. This amount will vary according to the activities undertaken on the day which can vary due to local weather conditions. Maximum travel fee is $40. This covers the cost of one vehicle only as Gould League Educators will carpool.
Student needs to bring: Their own water and lunch, sunscreen, a clipboard, pencil, and a copy of the Gould League workbook (usually sent 7 – 14 days prior to excursion so copies can be made for students) to guide the forest investigation; bag to take away your rubbish.
Restrictions: This Gould League program is delivered in the Toolangi State Forest, in the North Central Fire District and does not operate on days with a Fire danger rating of Extreme and Catastrophic. On rare occasions, programs may be postponed due to extreme weather predictions involving wind/storms. In both cases, these programs will be rescheduled at the earliest convenience of both parties.
Programs DO operate during wet/snowy weather. Please contact us to discuss the best timing to optimize your group’s experience and ensure suitable clothing and footwear for the conditions predicted. Plan for wet weather from April-October, and expect temperatures at least 5 degrees colder than suburban Melbourne.
Curriculum Links
Geographical Knowledge and Understanding – Water in the World
The classification of water as a renewable resource, the forms that it takes as a resource in the water cycle, and the ways in which flows of water connect and change places VC2HG8K01
The environmental, economic, cultural, spiritual and aesthetic uses and value of water, including for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples and peoples of the Asia region VC2HG8K02
The distribution and variability of Australia’s water resources and the forecasted impacts of climate change on them VC2HG8K03
The nature of water scarcity and ways of overcoming it, with examples from Australia, and West Asia and/or North Africa VC2HG8K04
The causes of, impacts of and responses to an atmospheric or hydrometeorological hazard VC2HG8K05
Geographical Knowledge and Understanding Place and liveability
The influence of environmental quality on people’s perceptions of the liveability of places VC2HG8K08
The influence of social connectedness and community identity on people’s perceptions of the liveability of places, including the cultural connectedness of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples to Country and Place VC2HG8K09
How the concepts of space, environment and interconnection can be applied to evaluate the liveability of a place
VC2HG8K10
Responses to enhance the liveability of places at a local scale VC2HG8K11
Geographical Skills – Geographical Inquiry
Collect, organise and process information and data from primary and secondary sources, including fieldwork, and using geospatial technologies and digital tools as appropriate VC2HG8S02
Interpret and analyse information and data to identify similarities and differences and explain patterns, relationships and trends VC2HG8S04
Geographical Skills – Concluding and decision-making
Consider ethical values and draw evidence-based conclusions based on the evaluation of the information and data on a geographical phenomenon, issue or challenge using the concepts of space, change, interconnection and environment VC2HG8S05
Understanding Science – Biological Science
Matter and energy flow through ecosystems and can be represented using models, including food webs and food pyramids; populations will be affected by changing biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem including habitat loss, climate change, seasonal migration and introduction or removal of species VC2S8U04
Understanding Science – Earth and Space Science
Earth is a dynamic planet as demonstrated by tectonic activity, including the formation of geological features at divergent, convergent and transform plate boundaries; the theory of plate tectonics is supported by scientific evidence VC2S8U10
Science Inquiry – Processing, Modelling and Analysing
Data and information can be organised and processed by selecting and constructing representations including tables, graphs, keys, models and mathematical relationships VC2S8I04 (Students use dichotomous keys to classify and identify terrestrial and water invertebrates)
Information and processed data can be analysed to show patterns, trends and relationships, and to identify anomalies VC2S8I05
Science Inquiry – Evaluating
Evidence-based arguments can be constructed to support conclusions or evaluate claims, including consideration of ethical issues and protocols associated with using or citing secondary data or information VC2S8I07
The Victorian Curriculum F-10 content elements are © VCAA, reproduced by permission. Victorian Curriculum F-10 elements accurate at time of publication. The VCAA does not endorse or make any warranties regarding this resource. The Victorian Curriculum F-10 and related content can be accessed directly at the VCAA website.
